Top 10 Open Source Vulnerabilities In 2020


If 2020 taught us anything, it’s to expect the unexpected. While there don’t seem to be enough words to cover the changes that we all did our best to adjust to, we are more than happy to give you our rundown of the top 10 open source vulnerabilities in 2020.
Remote or not, our talented and hard-working Knowledge Team combed through the Mend vulnerabilities database to find all of the new open source vulnerabilities published in 2020 to provide you with the most up to date info on security issues in the open source projects we all use. The Mend database continuously collects information from dozens of sources including the NVD, security advisories, and open source project issue trackers, to ensure the most comprehensive open source vulnerabilities coverage possible.
This year’s top ten list includes some of the most popular open source projects out there, used for a variety of applications and platforms throughout the SDLC. The Mend database includes millions of vulnerable files and packages, some indexed with a CVE prefix, and other with a WS prefix when the issue is yet to be added to the CVE index.
So here they are, our list of the top ten new open source security vulnerabilities published in 2020.
#1 Lodash

CVSS: 7.4 High
Affected versions: before 4.17.2
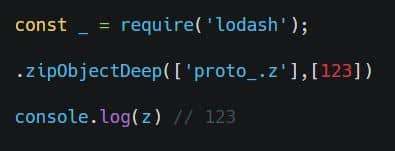
A prototype pollution security issue was found in vulnerable versions of Lodash, when using _.zipObjectDeep. According to the original report on HackerOne, the vulnerability could be exploited by an attacker to inject properties on Object.prototype. This could result in the disclosure of sensitive information, addition or modification of data, or Denial of Service (DoS). The HackerOne report provided these steps to reproduce:
Craft an object by “zipObjectDeep” function of lodash
Lodash is a JavaScript utility library that promises to deliver “modularity, performance, and extras.” Lodash documentation proudly states that Lodash makes JavaScript easier to handle by simplifying work with arrays, numbers, objects, strings, and more. That’s probably why so many developers love to use this open source library for iterating arrays, objects, and strings; manipulating and testing values; and creating composite functions.
You can learn more about the issue on the GitHub issue page, the NetApp advisory, and the NVD.
#2 FasterXML jackson-databind

CVSS: 8.1 High
Affected versions: 2.x before 2.9.10.6
Vulnerable versions of FasterXML jackson-databind mishandle the interaction between serialization gadgets and typing, related to br.com.anteros.dbcp.AnterosDBCPDataSource (aka Anteros-DBCP).
Serialization is a popular practice for Java developers, and over the past few years many serialization issues have been reported in Java serialization frameworks and libraries. According to @cowtowncoder, a prolific open source developer who is perhaps best known for the JSON library, “serialization gadgets” could perform malicious operations as side effects, opening the door to attacks like remote code execution, denial of service, or exposure of sensitive data. While this type of exploit has the potential of wreaking havoc, @cowtowncode also makes it clear that these types of attacks are not that easy to execute and require many prerequisites.
The much-beloved JSON parser for Java, jackson-databind has been a favorite for years thanks to the way it translates between the popular data exchange converter JSON and Java. When developers want to run an API and keep the lights on for users, jackson-databind is often their go-to.
If you, too, are a Java head, it’s best you make sure that your jackson-databind version is up-to-date. You can read more about this issue here, here, and here.
#3 HtmlUnit

CVSS: 8.1 High
Affected versions: prior to 2.37.0
Code execution issues were discovered in vulnerable versions of HtmlUnit. According to the NVD, when HtmlUnit initializes the Rhino engine improperly, a malicious JavaScript code can execute arbitrary Java code on the application. When embedded in the Android application, since Android-specific initialization of the Rhino engine is not performed properly, a malicious JavaScript code can execute arbitrary Java code on the application.
According to their documentation, HtmlUnit is a “GUI-Less browser for Java programs”, that also supports JavaScript and AJAX libraries. It models HTML documents and provides an API that allows users to invoke pages, fill out forms, click links, and more. This open source project is typically used for testing purposes or to retrieve information from web sites.
A fixed version is available on GitHub, and you can read more about the issue and its fix here, and here.
#4 Handlebars

CVE-2019-20920
CVSS: 8.1 High
Affected versions: before 3.0.8 and 4.x before 4.5.3
According to the npm security advisory, an arbitrary code execution security issue was found in vulnerable versions of Handlebars. The advisory explains that the package’s lookup helper doesn’t properly validate templates, which allows malicious players to submit templates that execute arbitrary JavaScript in the system. This vulnerability can be used to run arbitrary code in a server processing Handlebars templates or on a victim’s browser (effectively serving as Cross-Site Scripting). The vulnerability is a result of an incomplete fix for a previous issue.
Handlebars, an extension to the Mustache templating language, is a “logicless templating language that keeps the view and the code separated from one another” for an easier experience. Currently boasting over seven million weekly downloads from npm, it’s an extremely popular open source project, supported and maintained by a hard-working community that can be counted on to swiftly report and remediate any issues that are found.
#5 http-proxy

CVSS: 7.5 High
Affected versions: prior to 1.18.1
As we reported back in June, some versions of http-proxy are vulnerable to Denial of Service. An HTTP request with a long body triggers an ERR_HTTP_HEADERS_SENT unhandled exception that crashes the proxy server. This is only possible when the proxy server sets headers in the proxy request using the proxyReq.setHeader function.
Http-proxy is an HTTP programmable proxying library that supports websockets and helps to implement components like reverse proxies and load balancers. It’s an extremely popular open source library, currently boasting nearly 12 million weekly npm downloads, and supporting over 2,000 dependents. Considering those stats, there’s a good chance you are directly or indirectly using http-proxy, and it’s time to make sure that you are using an updated version.
The good news is that this issue has been fixed in 1.18.1. You can learn more about the fix in the pull request on GitHub.
This vulnerability’s ID begins with a WS rather than the more common CVE prefix, since the issue is yet to be listed in the CVE yet. While many see the CVE and NVD as the only resources for information about security vulnerabilities, some issues are first published elsewhere. Due to the decentralized nature of the open source community, open source vulnerabilities are often published in an advisory, forum, or issue tracker before being indexed in the CVE. These issues are added to the Mend database with a WS prefix.
When managing open source vulnerabilities, It’s important to keep in mind that relying exclusively on the CVE or NVD is not enough to fully cover all of the open source vulnerabilities in your code.
#6 decompress

CVSS: 9.8 Critical
Affected versions: prior to 4.2.1
According to the npm security advisory, affected versions of decompress are vulnerable to Arbitrary File Write. Malicious players could write to any folder in the system by including filenames containing../ because the package doesn’t prevent extraction of files with relative paths.
decompress is an open source project that makes extracting archives easy. This is an example of how a vulnerability in a relatively small project, used by many to perform a simple task, can cause massive damage to users when left un-remediated. Projects like decompress make coding easier for us, but as simple as the tasks they perform may be, they cannot be overlooked when it comes to open source vulnerabilities management.
In order to remediate this issue, the advisory recommends updating to version 4.2.1 or later. You can read more about this issue and its fix on GitHub.
#7 XStream

CVSS: 8.8 High
Affected version: before 1.4.14
A remote code execution issue was discovered in vulnerable versions of XStream. The XStream issue page explains: “The processed stream at unmarshalling time contains type information to recreate the formerly written objects. XStream creates therefore new instances based on these type information. An attacker can manipulate the processed input stream and replace or inject objects, that can execute arbitrary shell commands.”
The GitHub Security Advisory recommends that users that rely on XStreams default blacklist of the security framework update to version 1.4.14 or over. Users that followed the recommendation to set up XStream’s Security Framework with a whitelist, are not affected.
XStream is an open source library that performs Java to XML serialization, and back again. Documentation lists transport, persistence, configuration, and unit tests as typical uses. Since it’s a very popular library used by many large open source Java web applications, it’s very important to make sure that you are updating your versions and following advisory recommendations.
You can learn more about the fix on GitHub.
#8 Netty

CVSS: 9.8 Critical
Affected versions: 4.1.x before 4.1.46
The ZlibDecoders vulnerable Netty versions allow unbounded memory allocation while decoding a ZlibEncoded byte stream. A malicious player could exploit this security vulnerability to send a large ZlibEncoded byte stream to the Netty server, forcing the server to allocate all of its free memory to a single decoder.
Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework designed for fast-paced development of maintainable high-performance protocol servers & clients. According to the project’s documentation, this NIO client/server framework helps to simplify and streamline network programming like TCP and UDP socket server.
Read more about this issue and its fix on GitHub, here, here, and here.
#9 Spring Framework

CVSS: 7.5 High
Affected versions: 5.2.x prior to 5.2.3, versions 5.1.x prior to 5.1.13, and versions 5.0.x prior to 5.0.16
In affected versions of the Spring Framework, an application is vulnerable to a reflected file download (RFD) attack when it sets a “Content-Disposition” header in the response where the filename attribute is derived input supplied by the user.
If you’ve been using Java, you’ve most probably come across Spring. It’s a widely popular Java application development framework, thanks to how modular and lightweight it is, allowing developers to easily create powerful applications. It is well known for its inversion of the control design principle which incorporates layering, a lightweight container, and the ability to program on an interface.
You can read more about the issue here.
#10 PyYAML

CVSS: 9.8 Critical
Affected versions: before 5.3.1
Vulnerable versions of the PyYAML library are susceptible to arbitrary code execution when untrusted YAML files are processed through the full_load method or with the FullLoader loader. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code on the system by abusing the python/object/new constructor.
PyYAML is an extremely popular YAML parser and emitter for Python. Considering Python’s continuously increasing popularity over the past few years, it’s best to make sure that you’re using an updated version of PyYAML.
You can learn more about this issue and its fix here, and here.
New Year’s Resolution: Manage Your Open Source Security The DevSecOps Way
We all rely heavily on open source and third-party components that help us to develop and deliver innovative software products at scale and speed. Although application security has become a top concern for stakeholders, many teams unfortunately still view security as a heavy time-consuming task that slows them down.
We’re here to remind you that open source security is crucial to application security, and that contrary to popular belief, it doesn’t have to hinder rapid development. DevSecOps tools can help us integrate automated testing early and often in the DevOps pipeline, to ensure the open source components you rely on are secure and up-to-date without compromising on speed.
